Predicting Performance in PVC Inflatable Materials
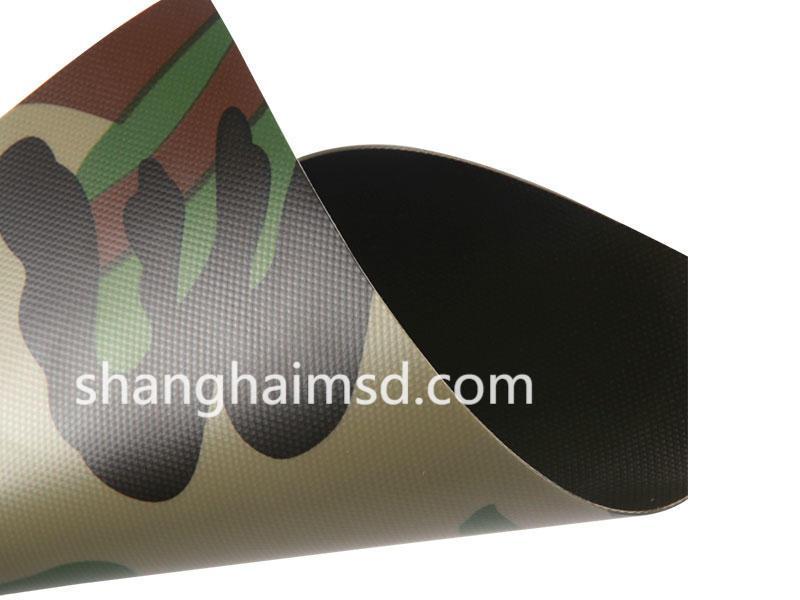
As inflatable products are increasingly used in commercial, industrial, and professional scenarios, durability has become a central design concern, and PVC Inflatable Fabric is frequently selected because it offers a controllable balance between flexibility and long-term mechanical reliability when properly engineered. Unlike rigid structures, inflatable systems rely entirely on material integrity to maintain form and function, making even small defects or inconsistencies potentially critical over time.
Durability begins with the interaction between the textile reinforcement and the PVC coating. The base fabric must distribute internal pressure evenly while resisting localized stress concentrations caused by seams, folds, and attachment points. Yarn selection, weave density, and fabric orientation all influence how stress propagates through the structure during inflation. If the textile layer exhibits uneven elongation, it can lead to coating microcracks that compromise air tightness long before visible damage appears.
The PVC compound itself plays an equally important role in long-term performance. Plasticizer migration, thermal aging, and environmental exposure can gradually alter flexibility and surface integrity. A formulation optimized only for initial softness may stiffen over time, increasing the risk of cracking during repeated folding or low-temperature use. For this reason, durability-focused materials often incorporate stabilizers designed to slow chemical degradation without negatively affecting weldability or surface finish.
Manufacturing consistency is a key factor in preventing premature failure. Variations in coating thickness, incomplete impregnation of the textile substrate, or uneven curing can all introduce weak points. During processing, precise temperature control ensures that the PVC penetrates the fabric sufficiently without damaging the yarn structure. Excessive heat may weaken the base fabric, while insufficient heat can result in poor adhesion between layers, both of which reduce service life.
Seams represent the most common failure zones in inflatable products, making seam design and execution critical. Stress at seams is not only influenced by internal pressure but also by user handling, torsion, and external loads. Reinforcement tapes, overlap width, and welding parameters must be matched to the material’s mechanical behavior. In durability testing, seam fatigue often reveals performance gaps that are not apparent in static strength tests.
Field conditions further complicate durability expectations. Inflatable products may be exposed to UV radiation, moisture, oils, or abrasive surfaces depending on their application. UV exposure can accelerate PVC aging, while moisture trapped between folded layers may encourage surface degradation if additives are poorly balanced. As a result, durability evaluation increasingly includes combined-environment testing rather than isolated laboratory conditions.
Quality control systems are essential for maintaining consistency across production batches. Visual inspection alone is insufficient; non-destructive testing methods such as air pressure retention monitoring and peel strength sampling provide more reliable indicators of long-term behavior. Manufacturers who integrate these checks into routine production can identify trends early, reducing the risk of large-scale failures after products enter service.
From a supply perspective, material traceability supports durability management. Knowing the exact formulation, fabric source, and processing parameters allows manufacturers to replicate successful designs and adjust quickly when performance issues arise. Shanghai MSD International Trade emphasizes this traceability by coordinating closely with material producers and downstream customers, helping ensure that material specifications remain stable across repeat orders and evolving applications.
As inflatable products continue to move into higher-value and higher-risk uses, durability engineering becomes less about maximizing individual properties and more about managing interactions across materials, processes, and real-world conditions. Designers and manufacturers seeking deeper insight into how PVC inflatable materials are structured, tested, and optimized can explore further technical explanations provided by Shanghai MSD through its industry knowledge resources at https://www.shanghaimsd.com/news/what-is-pvc-inflatable-fabric-everything-you-need-to-know.html .
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Spiele
- Gardening
- Health
- Startseite
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Andere
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness