When Should You Choose Specialized Aluminum Wire?
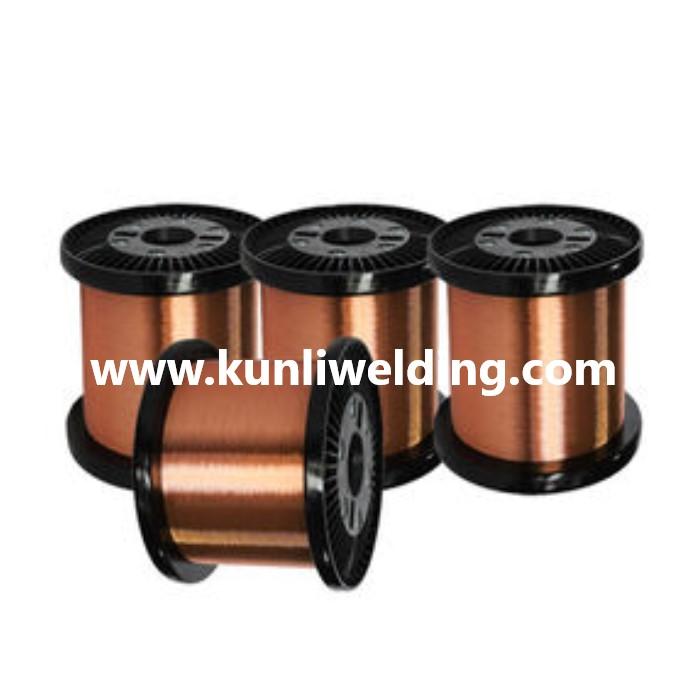

Material selection decisions for aluminum fabrication projects require evaluating whether standard general-purpose filler materials adequately serve application requirements or whether specialized formulations provide necessary performance advantages justifying their premium costs. While standard grades handle many common welding tasks reliably and economically, certain scenarios demand enhanced properties that basic materials cannot deliver across structural integrity, environmental durability, or operational performance criteria. Understanding when to specify specialized products from Kunli Aluminum Welding Wire Manufacturers rather than defaulting to standard options helps fabricators match filler capabilities to actual application demands, ensuring welded structures maintain integrity throughout component service life across demanding environments and loading conditions.
Corrosive environment exposure represents a primary consideration favoring specialized filler materials over standard grades in applications where environmental attack threatens structural integrity or creates safety hazards. Marine structures, chemical processing equipment, coastal infrastructure, and offshore platforms face aggressive conditions attacking materials lacking adequate environmental resistance through multiple corrosion mechanisms. Standard aluminum filler materials provide basic atmospheric corrosion protection suitable for indoor applications or mild outdoor exposure where moisture and pollutants remain minimal. Specialized chromium-bearing and enhanced magnesium formulations deliver superior resistance to saltwater immersion, industrial atmospheres, and chemical exposure through improved protective oxide film characteristics and electrochemical stability. When corrosion threatens structural capacity or creates operational disruptions with significant safety and economic consequences, specialized materials justify their incremental cost through extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements.
High-strength structural applications require weld metal approaching base metal mechanical properties, capabilities that standard filler materials may not adequately provide across demanding load-bearing scenarios. Aerospace components, performance vehicles, and engineered structures where joint strength directly affects load-carrying capacity demand filler materials producing weld metal strength compatible with high-strength base metals utilized for specific mechanical advantages. Specialized formulations with enhanced alloying provide the strength levels these applications require for structural integrity throughout operational lifecycles. Using standard materials in high-strength applications creates weak joints limiting overall structural capacity regardless of base metal strength, undermining design intentions and potentially creating safety hazards. Engineering specifications recognizing this limitation mandate specialized materials ensuring weld zones function as integral structural elements rather than weak links compromising overall assembly performance.
Elevated temperature service creates demands exceeding standard material capabilities as equipment operating in hot environments requires weld joints maintaining strength without excessive softening or creep deformation affecting structural stability. Heat exchangers, engine components, and industrial process equipment experiencing sustained elevated temperatures benefit from specialized filler materials formulated for thermal stability maintaining mechanical properties across temperature ranges encountered during operation. Standard grades adequate at ambient temperatures may soften excessively when heated, compromising structural integrity and potentially causing premature failures. Temperature specifications in design documents guide material selection, with specialized high-temperature formulations specified when service temperatures exceed standard material capabilities documented through qualification testing.
Crack-sensitive base metals or highly restrained joint configurations benefit from specialized filler materials engineered for enhanced crack resistance addressing hot cracking susceptibility during solidification. Certain aluminum alloys and welding scenarios exhibit hot cracking tendencies when thermal stresses exceed partially solidified metal strength during cooling from welding temperatures. Thick sections, rigid fixturing, and complex joint geometries create restraint promoting cracking despite proper welding procedures. Aluminum Welding Wire formulations specifically developed for crack resistance modify weld pool chemistry reducing cracking susceptibility in challenging applications through metallurgical solutions. While proper joint design and welding procedure development address cracking through multiple approaches, specialized filler materials provide additional metallurgical protection complementing procedural controls.
Color matching requirements after anodizing or other finishing treatments influence filler selection for architectural and decorative applications where appearance affects customer satisfaction and aesthetic design intent. Some filler and base metal combinations produce visible color differences after surface treatment, creating unattractive weld zones contrasting with surrounding material despite producing structurally sound joints. Specialized filler materials formulated for anodizing compatibility produce color-matched welds that blend with base metal after finishing processes. Applications where appearance influences product acceptance or aesthetic value justify specialized materials preventing visible weld zones that standard materials might create.
Dissimilar metal welding scenarios sometimes require specialized filler materials bridging compositional differences between varied base metals within complex assemblies. Fabrications combining different aluminum alloy families need filler chemistry compatible with both materials simultaneously ensuring metallurgical soundness across all joints. Standard fillers work across limited base metal ranges while specialized versatile formulations accommodate broader alloy combinations through carefully balanced chemistry. Complex structures incorporating castings, extrusions, and wrought materials of varied compositions benefit from specialized filler materials simplifying material management while ensuring compatibility.
Regulatory compliance and industry specifications sometimes mandate specialized materials based on qualification testing and approved material lists governing regulated applications. Pressure vessel codes, maritime classification requirements, and aerospace standards reference specific filler materials by designation based on documented performance in demanding applications and established qualification histories. Following specified materials ensures regulatory acceptance and design assumption validity supporting equipment certification. Standard materials, while technically adequate for basic mechanical requirements, may lack the qualification documentation and approval status that regulated applications absolutely require for legal compliance.
Understanding when specialized Aluminum Welding Wire provides genuine advantages versus when standard grades prove adequate enables informed selection balancing performance requirements against economic realities across fabrication projects. Applications genuinely requiring enhanced properties justify specialized materials through improved outcomes and lifecycle performance, while routine work benefits from standard material economics without sacrificing quality when properly applied within appropriate application boundaries. Detailed material specifications and selection guidance are available at https://www.kunliwelding.com/product/ .
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Juegos
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Other
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness